Vietnam Digital Technology Incentives 2025 – Tax, Employment & Visa Support
On 14 June 2025, the Vietnamese government enacted a dedicated digital technology law, the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025 (effective from 1 January 2025), to provide a foundation to further develop Vietnam’s technology industry. Within a relatively short timeframe, the Government has introduced and proposed several related regulations, including the Law on Corporate Income Tax 2025 (“CIT Law 2025”), the Law on Personal Income Tax 2025 (“PIT Law 2025”), and Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP regarding visa exemptions for special objectives for foreigners (“Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP”). This article consolidates the key provisions related to incentives and support for the digital technology sector and foreign digital technology personnel.
I. Tax Incentives for Digital Technology Corporations
Addition of certain sectors eligible for CIT incentives
Clause 2 article 12 of the CIT Law 2025 adds certain industries within the digital technology sector to the list of sectors eligible for Corporate Income Tax incentives, including:
• Production and provision of key digital technology products and services.
• Manufacturing of electronic equipment as stipulated by the law on digital technology industry.
• Research, development, design, production, packaging, and testing of semiconductor products.
• Construction of artificial intelligence data centres.
These sectors are eligible for a maximum tax exemption of 4 years, followed by a 50% reduction in taxable income for a maximum of 9 subsequent years (point a, clause 1, article 14 of CIT Law 2025). This is on top of a preferential tax rate of 10% for 15 years (point a, clause 1, article 13 of CIT Law 2025), which is half the standard rate of 20%.
To benefit from these CIT incentives, the investment project must be recognized as a “new investment project” and meet other criteria stipulated by law (e.g., the project’s products must be included in the list of key digital technology products and services, and meet the criteria for recognizing electronic equipment manufacturing projects). However, regulations defining these are yet to been released, and therefore, investors should monitor forthcoming implementing guidance for clarification on the requirements by the authorities before these incentives can formally be utilised.
II. Tax and Employment Incentives for Digital Technology Personnel
2.1 Digital technology personnel eligible for PIT incentives
Digital technology industry personnel (“digital technology personnel”) are defined in the Law on Digital Technology 2025 (clause 4, article 3), as “individuals with qualifications, skills, and specialized knowledge in the field of digital technology”. This field encompasses not only digital technology activities (such as production and service provision) but also management activities. Therefore, individuals eligible for Personal Income Tax incentives in the digital technology sector not only includes engineers producing products and employees providing associated services, but it also includes directors and deputy directors of digital technology companies.
Under the previous regulations, the Law on Personal Income Tax 2007 (“PIT Law 2007”) simply stipulated that the PIT rate for income from salaries and wages for residents in Vietnam follows a progressive tax scale ranging from 5% to 35%, depending on the tax bracket. Meanwhile, a fixed PIT rate of 20% applies to income from salaries and wages for non-residents in Vietnam.
The introduction of the Law on Digital Technology 2025 (clause 3, article 49) introduces a new tax incentive framework, intended to attract skilled professionals and support the development of the sector, by offering a 5-year PIT exemption for digital technology personnel, regardless of residency.
Clause 3, article 49 of the Law on Digital Technology 2025 limits the scope of preferential treatment. Specifically, only income derived from projects located in preferential areas (e.g., concentrated digital technology zones), projects in preferential industries (e.g., production of key digital technology products, semiconductors, etc.), or income from activities related to training digital technology personnel is eligible for the above tax incentives. This restriction means that not all individuals working in the digital technology sector automatically benefit from the incentives. Instead, eligibility is tied to the nature of the project or activity generating the income. Investors and employers should therefore carefully assess whether their projects and employee income streams fall within the defined scope, and they should monitor forthcoming implementing guidance for clarification on the recognition process.
2.2 Work permit exemptions (“WPE”) for high-quality digital technology experts
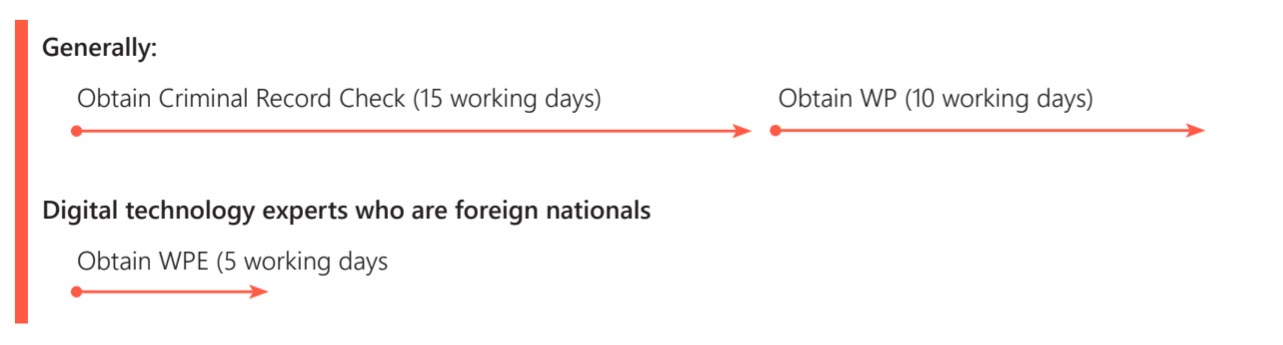
Under the general framework of the Labor Code 2019, foreign employees are required to obtain a work permit to work in Vietnam. At present, this process typically takes approximately 10 working days to complete (clause 3, article 22, Decree No. 219/2025/ND-CP), excluding the time required to obtain a criminal record, and to notarize or legalize the necessary documents.
Clause 4 article 49 of the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025 adds high-quality digital technology experts who are foreign nationals to the list of categories exempted from the work permit requirement. Instead of applying for a work permit, these individuals may obtain a confirmation letter certifying their exemption. The processing time is comparatively streamlined, with a reduced processing time of 5 working days and fewer dossier requirements (e.g., no criminal record submission), thereby saving significant time and effort in preparation.
However, it should be noted that the criteria for recognizing “high-quality digital technology experts” have not yet been detailed. It is expected that a guiding decree for the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025 will be issued shortly, providing investors with a basis to determine whether they/their employees qualify as high-quality digital technology experts, which will assist them to ascertain whether they/their employees are eligible for work permit exemptions.
2.3 Visa exemptions for special cases
Under the previous regulations, article 12 of the Law on Entry, Exit, Transit, and Residence of Foreigners in Vietnam 2014 outlined only five cases eligible for visa exemption (e.g., exemption under international treaties to which Vietnam is a party; exemption for holders of permanent or temporary residence cards).
The issuance of Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP has expanded the list by adding seven additional cases eligible for visa exemption, referred to as “special objectives requiring preferential entry into Vietnam,” which include high-quality digital technology experts (digital technology personnel must meet the conditions outlined in section 3 of this article to be recognized as a high-quality digital technology expert) as stipulated in point b, clause 1, article 2 of Decree No. 221/2025/NĐ-CP.
With a processing time of 5 working days – equivalent to the standard visa application process – the visa exemption procedure under Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP offers the following benefits:
Visa exemption period: Up to 5 years, but not more than 30 days shorter than the remaining validity of the passport (clause 4, article 4 of Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP). This means that for 5 years from the date of issuance of the visa exemption certificate, high-quality digital technology experts who are foreigner nationals, can enter Vietnam without a visa. Compared to the typical entry duration for regular workers (under visa types LD1 and LD2) (point c, clause 4, article 1 of the amended Law on Entry, Exit, Transit, and Residence of Foreigners in Vietnam 2019), the entry period for digital technology experts who are foreigner nationals is 2.5 times longer.

Issuance of a 90-day temporary residence confirmation per entry
Normally, the duration of a temporary residence confirmation ranges from 15 to a maximum of 90 days, depending on the purpose (clause 13, article 1, of the amended Law on Entry, Exit, Transit, and Residence of Foreigners in Vietnam 2019). The provision of a 90-day temporary residence period for high-quality foreign digital technology experts (clause 1, article 6 of Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP) represents the highest level of incentive, reflecting significant preferential treatment by the Vietnamese government toward this objective.
Additionally, clause 1, article 6 clarifies that if high-quality foreign digital technology experts wish to stay longer in Vietnam, they may still be considered for a temporary residence extension, visa issuance, or temporary residence card issuance, in accordance with the Law on Entry, Exit, Transit, and Residence of Foreigners in Vietnam 2014.
While the visa exemption regime is designed to facilitate the entry of high-quality digital technology experts, the application process remains subject to detailed administrative and documentary conditions. High-quality foreign digital technology experts must meet the visa exemption conditions specified in article 3 of Decree No. 221/2025/ND-CP, as well as the criteria for defining “high-quality digital technology experts” which are to be detailed in a forthcoming guiding decree under the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025.
2.4 Issuance of a 5-Year Temporary Residence Card for high-quality digital technology experts
Clause 2, article 19 of the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025 states that high-quality foreign digital technology experts, are eligible for a temporary residence card (“TRC”) with a validity of up to 5 years. In contrast, under the previous regulations (clause 16, article 1 of the amended Law on Entry, Exit, Transit, and Residence of Foreigners in Vietnam 2019), TRCs for workers (holding the visa LD1, LD2) were limited to a maximum validity of 2 years.
As a result, high-quality digital technology experts are entitled to a TRC with a duration 2.5 times longer than that of regular workers. Moreover, they have the right to extend their period of temporary residence, a privilege previously reserved only for certain individuals holding diplomatic visas (visas type NG1, NG2, NG3, NG4) (article 5 of Circular No. 04/2016/TT-BNG).

Notably, the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025 also provides additional incentives for the families of high-quality digital technology experts. According to clause 2, article 19 of the Law, spouses and children under 18 years old of high-quality digital technology experts are eligible for TRCs with a validity period equivalent to that granted to the high-quality digital technology experts. Furthermore, they are to be offered support in job placement, school enrolment, and education at educational institutions in Vietnam.
By providing a stable legal and social foundation, the above incentives seek to facilitate the settlement and long-term residence of high-quality digital technology experts and their families in Vietnam.
These recent legislative developments highlight Vietnam’s policy direction to promote the digital technology industry and to improve consistency across the legal framework. At the same time, they also indicate the Government’s effort to ensure that major structural focuses and announcements are accompanied by supporting laws and decrees to enable the formal implementation of the strategy across society.
It should be emphasized, though, that the Vietnamese Government still requires additional time to further refine the full legal implementation, such as issuing a guiding decree for the Law on Digital Technology Industry 2025 and the guiding decree for CIT Law 2025, and therefore the effectiveness of certain provisions remains pending. Accordingly, this article outlines the incentives and support measures currently provided under existing regulations, whilst future updates may bring further changes. Stakeholders should continue to monitor subsequent guidance closely so that they can take advantage of the available incentives.
For any further questions you may have, please reach out to us at vietnam@alitium.com
Article by: Nguyen Hoang Yen Nhi – Legal Assistant, Alitium
********
This article is intended to provide an overview of recent updates and announcement. While it aims to present useful insights, it is important to note that the content shared here should not be considered as formal legal or financial advice. For specific guidance on tax obligations or legal matters related to your business, we strongly recommend consulting with a qualified professional, such as a tax advisor or legal expert or directly reach out to us.








